
To demonstrate the usefulness of the circular flow model, let’s follow a few dollars through a cycle. The circular flow model highlights the “flows” within the economy-the flow of economic resources, goods and services, and the flow of money. One of the most useful is the circular flow model. Luckily, economists have developed models to help us learn and understand how the economy functions. Let’s face it, the economy is complex and can be difficult to understand. Read more about our award-winning resources » This video received the 2015 Curriculum Silver Award from the National Association of Economic Educators and was a 2014 Gold Winner of the AVA Digital Awards.
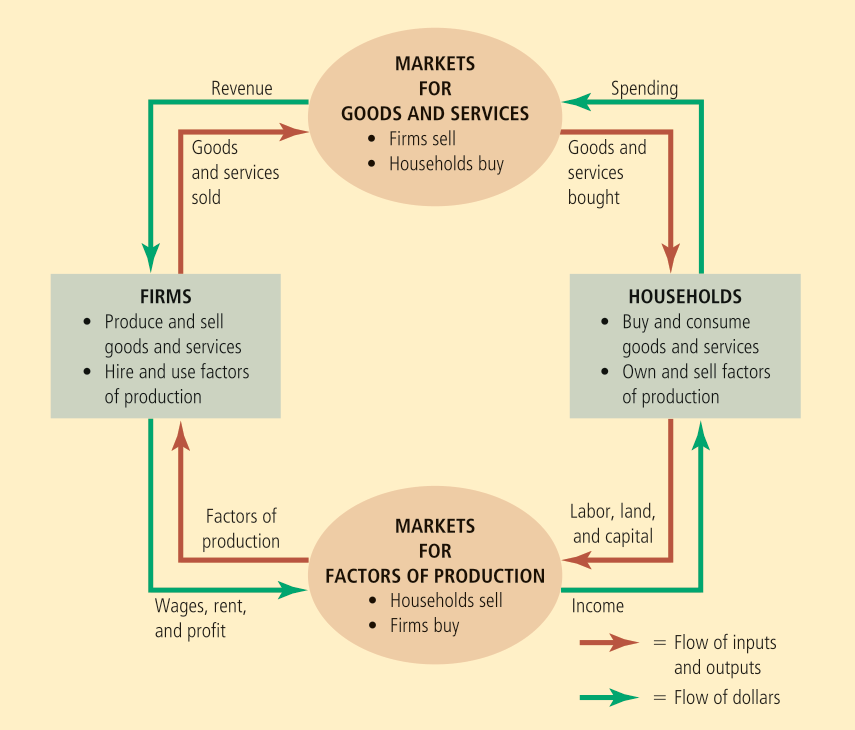
The most well-known theories are probably those of supply and demand, but you will learn about several others.More episodes featuring economic concepts: Both microĪnd macroeconomics are explained in terms of theories and models. In this way, these graphs serve as models to make inferences about behavior.Īt the introductory level, you can sometimes figure out the right answer without using a model, but if you keep studying economics, before too long you'll encounter issues and problems whose solution will require graphs. They use the graph to help them discover the answer. Counter to what you might expect, economists don't figure out the solution to a problem and then draw the graph. In economics, theories are expressed in models as diagrams, graphs, or even as mathematical equations. Then they use the theory to give them insightsĪbout the issue or problem. When economists identify an economic issue or problem, they sift through the available theories to see if they can find one that fits. Much the same way as a carpenter might grab a tool. We could easily add details to this basic model if we wanted to introduce more real-world elements, like financial markets, governments, or interactions with the rest of the world (imports and exports). Of the circular flow model is stripped down to the essentials, but it has enough features to explain how the product and labor markets work in the economy. This is shown in the inner circle, which represents the two sides of the labor market , in which households supply and firms demand. Households (as workers) sell their labor to firms in return for wages, salaries, and benefits.
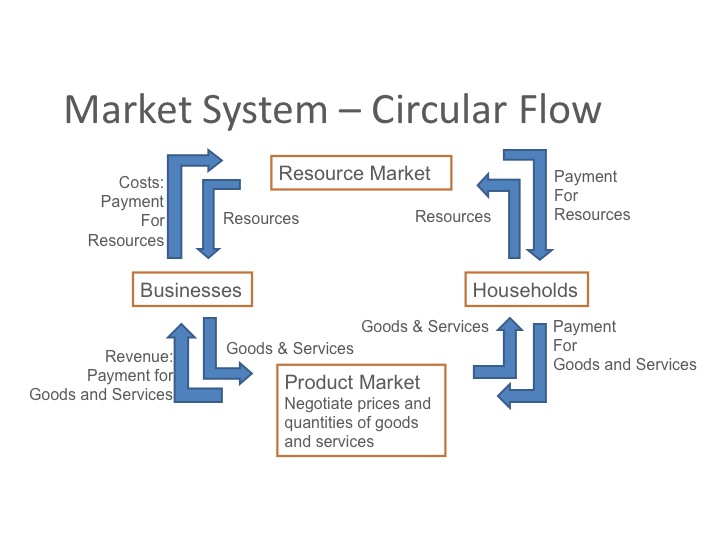
The outer ring represents the two sides of the product market (which provides goods and services), in which households demand and firms supply. In the diagram,įirms produce goods and services, which they sell to households in return for payments. The circular flow diagram simplifies these distinctions in order to make the picture easier to grasp. Of course, in the real world, there are many different markets for goods and services and markets for many different types of labor. Such a diagram indicates that the economy consists of two groups, households and firms, which interact in two markets: the goods-and-services market (alsoĬalled the product market), in which firms sell and households buy, and the labor market, in which households sell labor to business firms or other employees. Similarly, economic models offer a way to get a complete view or picture of an economic situation and understand how economic factors fit together.Ī good model to start with in economics is the circular flow diagram (Figure 2, below). Such models help people visualize a product (or a building) in a more complete, concrete way than they could
That are rougher and less finished than the final product but can still demonstrate how the new product will work and look. Companies often build models of their new products An architect who is designing a major office building will probably build a physical model that sits on a tabletop to show how the entire city block will look after the new building is constructed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
